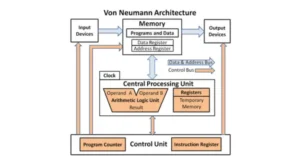
IoT in manufacturing revolutionizes production by connecting intelligent sensors, machines, and systems that communicate seamlessly to optimize every aspect of the manufacturing process. These tools include sensors and tools that may interact with one another. This makes tasks easier and faster. It is known as smart production. It is part of a larger trend known as Industry 4.0. This means that factories are becoming ever digital. This process is known as the digital shift. Machines in connected factories talk data with workers to help them make superior choices. This is also known as “factory digital.” It reduces errors and saves time. Industrial machine make becomes faster and less cheap. Companies may work more effectively and effectively with smart linked factories.
Why Smart Factories Need IoT
Smart factories need the Internet of Things to function properly. They use methods such as Industrial IoT (IIoT) and cyber- physical systems (CPS). These enable machines and computers to work together properly. This allows for easy automation. It also creates robust digital systems. Smart factories are able to change plans quickly. This is referred to as business agility. It enables people to cope with issues and go on. They can also test new ideas fast. This is known as innovative adoption. All of this lends them an unfair edge. It means they can surpass others. It also aids in futureproofing. So, smart factories are prepared for whatever happens next.
How to Get Started with IoT in Manufacturing
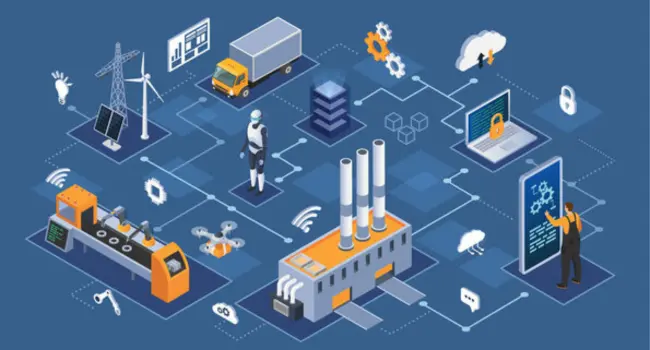
To get started with IoT, thoroughly plan your production needs. Choose the appropriate IoT sensors and tools. Start with a tiny project, train your employees, and then gradually expand your smart factory.
Plan Your Factory Needs
Before you begin, examine your factory’s activities. Consider what challenges you wish to solve. Do you wish to improve supply chain visibility? Or do you wish to save money through lean manufacturing? Determine how prepared your factory is for smart tools. This is known as digital maturity. Create a clear plan. It should involve strategic workforce deployment. This includes ensuring that the correct people are doing the proper jobs. Good planning helps you prevent problems later. A solid start makes things easier. When you understand your needs, you may select the appropriate tools and processes to begin your smart journey.
Pick the Right IoT Tools
Choosing the correct tools is crucial. Start with IoT and smart sensors. They get data from machines. Use RFID and RFID tags to track goods in real time. Smart factories use popular devices such as the Digi IX40, Digi XBee modules, and Digi Connect Sensor+. These tools allow you to see what is happening at each step. To link all devices, you’ll also need high-performance routers and gateways. These keep your system running quickly and smoothly. Good tools simplify work and help your manufacturing become smarter. So, choose carefully and ensure that everything works nicely together.
Try a Small Project First
You do not have to change everything at once. Begin with a modest assignment. Automate simple tasks, such as turning off machines when they are not in use. This provides quick results. It also contributes to meeting the need for quick deployment. To resolve issues from a remote location, try over-the-air (OTA) firmware updates. You can also try virtual machining to complete tasks digitally. Use digital work instructions to guide employees step by step. A modest project enables you to learn and flourish. It also demonstrates which methods work best before implementing them throughout the production. This makes adjustments feel secure and uncomplicated.
Train Workers and Keep Learning
Your employees are really crucial. They must comprehend how new tools work. Provide workforce training and upskilling. Teach employees how to use ergonomic automation to make their tasks easier and safer. Help them understand how humans and machines interact. Use augmented reality training to demonstrate steps clearly. This makes learning enjoyable and simple. In a smart factory, learning never ends. The more your employees know, the more efficiently your manufacturing will run. Helping others grow benefits your business as well. Continue training and improving every day. clever factories require clever, skilled employees.
Grow Your Smart Factory Step by Step
Do not rush. Effective factories take time to build. Use agile operations to improve gradually and safely. Make sure your plans include scalability so that your factory can expand effortlessly. Try ongoing development by resolving little issues every day. Use demand-driven manufacturing to provide what consumers require when they need it. Also, employ smart warehousing to store items more efficiently and conserve space. Growing gradually makes things run more smoothly. It also lowers tension. Each sensible change leads to further success. Small measures might transform your factory into a smart one. With time, your factory will get stronger, smarter, and more future-ready.
Key Benefits of IoT in Manufacturing
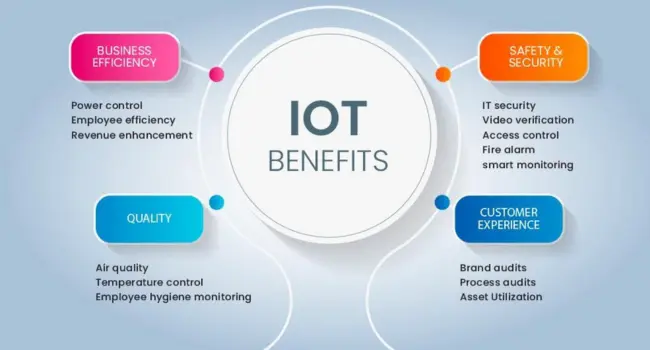
The Web of Things allows firms to constantly track machines. It increases product quality and keeps tools from breaking. It saves workers, saves money, uses less energy, and enables quick choices.
24/7 Real-Time Monitoring
With IoT, manufacturers may operate all day and night. Machines are monitored in real time. This means that personnel can identify problems before they worsen. Real-time data tracking, dashboards, and analytics are all useful tools for tracking machines. They show how everything works in real time. If any goes wrong, staff are quickly notified. This prevents delays. It ensures the factory runs smoothly. Real-time tools help to avert major issues. They also help to quickly resolve minor concerns. Always checking machines improves the factory’s safety and efficiency. It’s as if you’re always watching the machines.
Better Quality Control
The Internet of Things contributes to the creation of better products. It strengthens and accelerates quality control measures. Smart equipment may detect microscopic flaws in products. This is known as defect detection. Some instruments can even perform welding quality analysis to determine whether a weld is robust. These gadgets perform better than the human eye. They identify problems early. This helps to resolve problems before they leave the production. It also helps to reduce trash. Customers are pleased when they receive high-quality products. It saves both time and money. With IoT, factories can produce high-quality items over and over. Quality improves with little effort.
Reduced Downtime and Fewer Breakdowns
Stopping machines costs both time and money. IoT helps to reduce downtime. It employs predictive maintenance to repair equipment before they fail. This means that machines are checked early. Fault detection tools alert workers when something is incorrect. This ensures that the factory continues to operate. It also leads to lower maintenance costs. Fixing minor difficulties is less expensive than repairing major ones. Less downtime means more products are produced. Workers remain busy, and consumers receive orders on time. The Internet of Things allows things to run longer and more efficiently. Smart maintenance reduces factory downtime and costs.
Improved Worker Safety
The Internet of Things makes manufacturing safer. It promotes worker safety and workplace safety. Smart tools look for risk. They observe air, heat, and noise. They alert workers before things become dangerous. The Internet of Things can also handle dangerous task automation. This indicates that machines can perform dangerous tasks instead of humans. Safety monitoring tools ensure that everything remains safe at all times. Workers avoid harm. They feel more secure in their careers. A secure factory is a happy factory. Safety also results in fewer accidents. That allows everyone to work more effectively and quickly.
Lower Operational Costs
The Internet of Things helps factories save money. This is known as cost minimization. When machines perform better, workers can accomplish more in less time. That is known as productivity improvement. Better effort leads to more items and fewer mistakes. Factories spend less time addressing faults. All of this contributes to a higher ROI (return on investment). It signifies that money spent generates additional money. Smart gadgets help you conserve energy, save time, and reduce waste. These savings add up. IoT makes factories smart and low-cost. Spending less while doing more benefits any business.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
The Internet of Things helps manufacturers use less energy. This is referred to as energy efficiency. Smart tools turn tools on and off at the proper times. They also keep track of the amount of power used. This reduces the carbon footprint, which is helpful to the world. Green output produces less power and waste. Sustainable manufacturing refers to the creation of long-lasting products. It protects our planet and saves money. Using smart energy tools keeps the factory robust and green. IoT enables makers to be more environmentally conscious while creating higher-quality output. Going green benefits both businesses and nature.
Flexibility and Customization
IoT gives factories the ability to change quickly. This is known as flexibility. If a consumer requests something different, the factory can adjust swiftly. That’s known as customisation. The Internet of Things facilitates just-in-time manufacturing, which implies producing things just when they are needed. This saves both space and time. Workers and machinery don’t get stuck on previous designs. They can switch to new ones at any time. This enables factories to service more customers with fewer delays. It also prevents overproduction. Smart changes enable factories to perform more with less. IoT makes it simple to create what people want, when they want it.
Better Decision-Making with Data
The Internet of Things provides factories with a wealth of useful information. This is known as data-driven decision-making. Managers employ contextualized data insights to better comprehend what’s going on. These concepts are simple to read and apply. They also provide performance metrics—numbers that indicate how well things are running. Managers can use this information to make informed decisions. These are clever ideas that they can put into action. With the correct data, factories can make smarter decisions. Decisions are made with greater speed and intelligence. Good data helps to prevent problems from occurring in the first place. It also shows areas for improvement. Every day, the Internet of Things helps factories stay one step ahead.
Scalability for Business Growth
IoT enables factories to grow without stress. This is known as scalability. As the business grows, so can the factory. KPI monitoring allows you to keep track of important numbers. One such tool is Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE). It assesses how well machines are functioning. Smart tools enable factories to grow incrementally. IoT enables this type of corporate growth. You do not need to recreate everything. Simply add what you need as you need it. This saves both time and money. The Internet of Things ensures that your factory is always ready for expansion. Growth becomes simple and intelligent.
How IoT Works in Smart Factories

IoT connects machines and smart sensors in creation. It takes data and applies real-time insights to aid automate and control. It gets faster and smarter thanks to cloud and edge computing.
Connected Machines and Smart Sensors
In a smart factory, machines are not alone. They become networked devices capable of communicating with one another. This is known as machine-to-machine communication. It facilitates the rapid exchange of information. Machines contain embedded systems and smart sensors. They collect data and send it immediately. These sensors are small yet powerful. Some sensors are wireless, which means they don’t require connections. They are ideal for hard-to-reach locations. All of these tools help machines remain smart, attentive, and prepared. When everything is connected, the production functions more smoothly and efficiently, with fewer difficulties.
Data Collection and Real-Time Insights
Smart factories capture a large amount of information. This is known as machine data. It originates from sensors and machines. All of this data is sent to computers for analysis. They employ huge data and advanced analytics to figure out what’s going on. If something goes wrong, root cause analysis can help identify the source of the problem. Data visualization techniques such as graphs and charts are used to present the data. This makes it easier to identify patterns and resolve concerns. Managers may make rapid and informed decisions using real-time insights. Every day, data allows the manufacturing to be stronger, safer, and smarter.
Automation and Remote Control
The Internet of Things enables manufacturing automation. It indicates that machines can complete tasks without human oversight. Automated methods, such as automated assembly lines, make work more efficient and easy. Cobotics, often known as joint robots, operate along humans. They work hard. Workers do less heavy work while staying safe. Also, IoT allows for remote control. That means you can control tools from a computer or phone, even if you are not present in the work place. Everything gets simpler. Smart robotics conserves time and energy. It also allows factories to run all day with less effort from workers.
Role of Cloud and Edge Computing
Smart factories require a location to store and manage data. That’s where cloud computing can help. It protects massive volumes of information online. Many people use cloud-based data platforms or managed IoT cloud systems to handle everything. Certain chores, however, must be completed quickly. This is why edge computing is used. It works in close proximity to the equipment, eliminating the need to wait for the cloud. Edge AI also helps by making quick choices near the machine. Cloud and edge technologies work together to make smart factories faster, safer, and more powerful. They enable machines to think and act immediately.
Technologies That Support IoT in Manufacturing

Many tools assist the use of IoT in creation. These include fast routers, compact smart laptops 5G internet, cloud services, and robust data protection.
High-Performance Routers and Gateways
High-performance routers and gateways are critical in smart factories. They facilitate the seamless communication of all equipment and devices. These gadgets ensure that the plant is always linked. They transmit and receive data swiftly, so nothing is lost. Smart devices function more effectively when they have robust connections. They also assist the system remain safe and stable. These routers are designed to do multiple jobs at once. In a nutshell, they are the hub of communication in a smart factory. Without them, the machines would not function as a team. Good connections result in higher factory performance.
Smart Embedded Systems
Smart embedded systems are tiny computers that run inside machines. They help machines think and act intelligently. These systems collect data, send signals, and help control how the machines function. They require little space and work continuously. Even though they are little, they are extremely powerful. Smart embedded systems enable faster tasks and improved performance. They are integrated into all smart factory tools. These systems make machines safer, faster, and more useful. In smart factories, practically every gadget makes use of them. They are quiet helpers who keep the entire system working properly.
Cloud Platforms and IoT Managers
Cloud platforms are internet methods for storing data securely. They are utilized in cloud manufacturing to control everything from a single location. These platforms gather data from smart machines. Then they organize it so that others can better grasp it. IoT managers assist control devices and keep things functioning smoothly. They enable factories to expand without the need for a large investment in hardware. Everything becomes easily accessible from anyplace. You don’t have to be inside the facility to observe what’s going on. With cloud assistance, smart factories become faster, safer, and more organized. It’s like having a digital brain that runs the entire system.
5G and Better Connectivity
5G enables super-fast internet in smart industries. Machines may send and receive data at high speeds via 5G networks and private LTE/5G networks. This translates to less waiting and more doing. These networks support mobile IoT connectivity, allowing even moving machines to remain connected. Everything runs more smoothly with stronger signals and improved coverage. Even large data files can transfer in seconds. This allows for real-time control. Workers and robots can communicate without delay. 5G enhances smart factories. It provides faster speeds, stronger signals, and additional ways to connect. That’s why 5G is critical for future factories.
Cybersecurity for IoT Devices
IoT cybersecurity protects smart factories from hackers. Every smart device need protection. Secure IoT architectures are unique designs that prevent malicious users. They ensure that only the appropriate personnel can access the data. Advanced identity authentication systems verify user credentials and device permissions, creating multiple security layers that protect against unauthorized access to critical manufacturing systems. Data encryption is used to protect information so that others cannot read it. This protects factory secrets. Cybersecurity protects both workers and machines. Smart tools can be misused if they are not properly secured. That is why each smart factory need a strong protection. Good protection equals peace of mind. It ensures that the entire system remains safe, operational, and trusted by everyone who use it.
Blockchain for Data Security
Blockchain is similar to a digital notebook that no one can modify. It stores every data securely and clearly. This helps with blockchain for IoT by ensuring that all device operations are tracked. If someone tries to update data, it is immediately displayed. Blockchain for supply chain is also useful. It facilitates tracking each product from start to finish. This makes everything easier to check. You always know where things are and who has handled them. Blockchain builds confidence in smart factories. It secures data, promotes honesty, and prevents cheating. That’s why factories utilize it to keep data secure and clear.
AI and Edge Computing in IoT
Artificial intelligence (AI) enables robots to learn and make choices. It enables AI-powered automation in production, making jobs faster and smarter. Applied machine learning and Deep Learning enable machines to continuously improve their performance by analyzing production patterns and optimizing processes in real-time. They examine data and improve on their own. Cognitive computing enables machines to grasp complex activities. Edge computing works near to the machines. It makes decisions quickly without waiting for cloud servers. This saves time and helps everything work smoothly. AI and edge make factories smarter. They can solve issues rapidly and make fewer mistakes. They work as the brain of smart factories.
Challenges of IoT in Manufacturing

Using IoT for industrial purposes might be tricky. There are issues such as data security, dear expenses, and making sure the network works correctly. Workers need proper training.
Data Privacy and Security Risks
Smart factories capture a large amount of information. This raises data privacy problems. If hackers gain access, they can steal sensitive data. These cybersecurity dangers are really serious. Factories must carefully protect their systems. They employ special tools and secure passwords. Employees must learn how to keep data secure. Data loss or theft can lead to catastrophic results. Protecting privacy helps to keep workers, machines, and products safe. Factories need to constantly look for emerging dangers. Good security is essential in smart factories to prevent bad actors from inflicting harm.
High Setup Costs
Starting a smart factory is not inexpensive. The high deployment costs can be a major issue. Purchasing smart tools and setting up equipment requires money. The initial investment is high, particularly for small businesses. They may not have sufficient finances. Sometimes the cost prevents industries from becoming smart. It is critical to plan ahead of time and adhere to a budget. Factories must see long-term savings from IoT. Smart factories can save money in the long run, even though they are initially pricey. Even still, many factories struggle to afford new technologies.
Connecting with Old Machines
Many factories use ancient machines. These are known as legacy systems. Connecting these aging machines with modern smart tools is difficult. This is known as legacy system integration. Older machines do not always operate well with newer gadgets. They may need special adapters or software. However, integration is not impossible. With the proper assistance, firms can connect old and new machines. This requires time and strategy. When done correctly, it makes the entire factory smarter. Combining old and new allows firms to save money and improve gradually.
Need for Skilled Workers
Smart factories require personnel who understand how to use new tools. There are often skill shortages. This means that staff do not always have the necessary training. Learning how to use IoT devices is essential. Factories must offer workforce training and upskilling. This boosts workers’ confidence and allows them to perform better at work. Skilled personnel ensure the factory’s safety and productivity. Problems may arise if the necessary skills are not in place. Closing skill gaps is a significant problem, but it also represents an opportunity to increase worker capacities and manufacturing success.
Handling Big Data
Every second, smart factories create a large volume of data. The process of managing this data is known as data management. Handling large amounts of data is difficult. This is often referred to as Big Data. Industries must collect, store, and analyse data quickly. If data is not handled properly, it might result in delays or errors. Good storage solutions help you organize and use your data properly. They enable managers to see what is going on and make informed choices. Managing massive data is difficult but critical for keeping factories work smoothly and efficiently.
Keeping Everything Connected
Smart factories need reliable connections. However, network reliability can be an issue at times. Machines can’t interact with one another if the internet or network is down. This creates delays and mistakes. Network problems cause factories to run slowly. Network splitting is sometimes used to keep various parts of the network distinct for safety concerns. However, this may make dialogue more difficult. Factory networks must be robust and ongoing. Keeping everything connected is difficult, but vital for smart factories to work properly.
Future of IoT in Manufacturing

In the future, factories will incorporate more robots and smart systems. They will conserve energy and employ techniques such as augmented reality (AR) to assist workers. Factories will become faster and safer.
More Automation and Smarter Factories
In the future, industries will employ greater autonomy from systems. This means machines will use autonomous decision-making capabilities to operate independently, reducing human intervention while maintaining optimal performance. Autonomous assembly will allow for faster and smarter creations. Robotics and industrial robotics will play an important role. Robots will perform a variety of tasks in a safe and efficient manner. They will help factories become more efficient. This will reduce errors and saves time. Smart factories will rely on these systems to work properly. Automation will make things easier for both humans and machines. Factories will become more modern and efficient at creating goods.
Sustainable and Green Manufacturing
Future factories will be greener. To protect nature, they will abide by ecological compliance rules. Monitoring the atmosphere will ensure that the air, water, and waste are clean. Control of energy and efficiency can lead to power savings. Factories can use less energy and emit fewer harmful emissions. Zero waste involves making less rubbish and reusing more. This helps to maintain the planet’s health. Production that is green benefits both the economy and our planet. Smart factories will strike a balance between output and sustainability. This will enable factories to grow in a clean and safe manner.
Rise of AR, AI, and Robotics
Augmented Reality (AR) and the use of virtual reality will benefit workers in smart production. AR can show workers what to perform step by step, easing difficult procedures. Virtual reality helps training via safe practice areas. Robots and robots will interact far better with humans than ever before. These tools enable people to learn faster and perform jobs safely. The use of mixed reality, machine learning, and robotics will bring about modern factories. Workers will feel supported, and machines will become more useful. This technology will make factory jobs far smarter and safer.
Smarter Decision-Making with Real-Time Data
To plan ahead, future factories will employ predictive analytics. This aids to detect problems before they occur. Anomaly detection tools monitor machines and quickly identify anything strange. Managers will have access to real-time data, letting them to make sensible choices quickly. This allows factories to run nonstop. Data tools will display clear facts, allowing you to solve problems early on. Intelligent production will prevent large-scale issues and reduce waste. Better selections will allow factories to save money and time. Real-time data will be critical to make factories more rapid, secure, and smarter in the future.
Servitization: Selling Services, Not Just Products
In the future, factories will sell more than simply goods. They will also provide services such as repair, upgrades, and support. This process is known as servitization. Customers will receive assistance in maintaining the functionality of their products. Even after the things have been sold, factories will maintain contact with their clients. Customer service automation powered by IoT enables factories to provide 24/7 support, automatically scheduling maintenance, sending usage alerts, and resolving common issues without human intervention. This promotes trust and long-term connections. Offering services will increase the value of things. It will provide new ways for factories to make money. Servitization makes factories more adaptable and customer-oriented. It alters how factories conduct business by combining products with helpful services.
Final Thoughts
IoT in manufacturing is the future. It allows factories to work more smoothly and quickly. It also makes the workplace safer for workers. IoT saves energy and protects nature. IoT simplify everything from the first plan to scaling up. There are some issues, but the benefits of much trump them. Smart factories employ IoT to remain strong and ready for the future. Overall, IoT enables factories to work smarter, safer, and cleaner. It greatly benefits the entire factories industry.
Common Questions about IoT in Manufacturing

How is IoT used in factories today?
IoT is used to manufacture electronics, food, cars, and planes. It also aids in tracking of gear used in build.
What problems does IoT solve in manufacturing?
The Internet of Things helps manufacturing run more efficiently. It improves the supply chain and work flow. It speeds up the production of high-quality items.
Can IoT reduce factory downtime?
Yes, IoT monitors machines to detect problems early. It can detect when tools require repair so that machines do not fail.
How does IoT help with safety?
The Internet of Things enables humans and robots to collaborate safely. It employs computerized models and alarms to keep workers safe.
How is predictive maintenance done using IoT?
IoT employs advanced methods to detect machine problems early on. It allows machines to be mended quickly, avoiding major problems.
Is IoT helpful in aerospace manufacturing?
Yes, IoT helps monitor airplane parts and tools. It keeps everything safe and in functioning order.
How can manufacturers improve PCBs using IoT?
Sensors are used in the Internet of Things to detect faults with PCBs early on. This saves time and money while creating them.