Complete Guide to Von Neumann Architecture Today
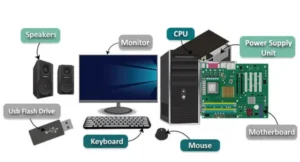
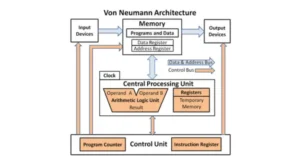
Von Neumann architecture is a design for how computers operate. In 1945, John von Neumann first explained it. It forms the basis of modern computers. This design employs the stored-program notion. That implies a computer can store instructions in memory and execute them as needed. A stored-program computer is adaptable. It can do a variety of functions. This design demonstrates how computers think and execute commands. It is a design for computer organization. Understanding it allows us to grasp why computers occasionally slow down. It also allows us to improve them in the future. What is Von Neumann Architecture? Berkeley system is another name for von Neumann architecture. It serves as a basis for most of modern electronic computers. It was first explained by John von Neumann in the EDVAC Report’s First Draft. It drove the growth of early computers such as the ENIAC, EDSAC, and IAS machine. This design is intended to support broad-application computing. Many programs can be run on a computer with stored programs. The CPU, memory, and input/output devices all work together to power the computer. This structure allows for great flexibility. Knowing it allows us to learn how computers analyze data and obey commands. It is the fundamental blueprint for modern computers. Basic Structure of Von Neumann Architecture The basic structure of Von Neumann architecture depicts how a computer operates. It is split into four main parts: the CPU, memory, buses, and input/output devices. Each piece has a certain function. The CPU thinks and makes decisions. The memory unit is used to store directions and data. Buses are used to move data between sections. Input/output devices allow robots to interface with humans. This concept employs a shared memory system, making computers simpler and simple. Knowing this structure enables us to grasp how robots process information and complete tasks. It serves as a model for most current computers. Central Processing Unit (CPU) The CPU, or processor, is the brain of the computer. It controls all operations and processes instructions. A CPU has many parts to work efficiently. Its configuration affects CPU performance and speed. Modern computers use microprocessors or general-purpose processors. The CPU reads instructions, performs calculations, and sends results to memory or devices. It works very fast, following the CPU clock speed. This central processing unit manages everything a computer does. Understanding the CPU helps us know how computers think and make decisions. It is the key part of the Von Neumann architecture. Registers These are little bits of highly rapid data inside the CPU. They store data only while the CPU works. The program counter (PC), instruction register (IR/CIR), and accumulator (ACC) are all critical processor registers. The memory address register (MAR) and memory info register (MDR) facilitate the transfer of data to and from memory. All-purpose registers are used to store interim results. These small storage spaces allow the CPU to run swiftly without the need for slower memory. Knowing registers shows how the CPU safely handles instructions. Processor registers are critical to a computer’s speed and ease of use. Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU) The CPU has an arithmetic logic unit (ALU). It does arithmetic operations such as adding or subtracting. It also performs logic processes, such as comparing numbers and making decisions. The ALU solves problems using interim register results. The ALU executes all requests that require analysis. This device allows the CPU to process data and make choices. The CPU cannot complete tasks unless the ALU is present. Knowing the ALU allows us to fully comprehend how computers perform math and logic fast within the CPU. Control Unit (CU) The control unit (CU) manages the CPU’s functions. It transmits control signals to other sections of the CPU. Timing signals guarantee that instructions are performed accurately. The CU also decodes instructions and understands what each command implies. It manages the ALU, registers, memory, and I/O devices. This element acts like a conductor in an orchestra, ensuring that everything functions together. Without the control unit, the CPU cannot work correctly. Understanding the CU allows us to see how computers manage things step by step. CPU Clock Speed CPU clock speed indicates how quickly the processor functions. It is measured in gigahertz (GHz). Each CPU clock cycle enables the CPU to execute one instruction. Higher clock rates result in speedier performance, but they also generate more heat. CPU clock speed influences how quickly applications run. Faster clocks enable the CPU to handle several jobs in a shorter time. Understanding clock speed allows us to compare processors and their performance. It is a critical component in the efficient design and operation of computers. Memory Unit The flash drive keeps data as well as instructions in the same place. This makes coding easy and adaptable. Computers employ main memory, which is also referred to as major memory or RAM. Shared memory allows the CPU to easily access orders and data. Memory safety ensures that apps do not erase each other. A good memory unit boosts computer speed. Understanding the memory unit reveals how systems store and retrieve info. Memory Hierarchy This structure classifies memory into tiers. DRAM main memory is fast and used for running programs. Flash memory can store data even when the machine is turned off. High Speed Memory (HBM) is very fast and aids in high-end activities. Its layout enhances computer efficiency. Delays fall with faster memory at the top. Knowing the memory hierarchy shows how computers balance speed and storage. Caches Caches are small, high-speed memory blocks within the CPU. L1 cache includes both an instruction cache (L1i) and a data cache (L1d). L2 and L3 caches are larger, but slightly slower. Caches contain frequently used instructions and data. This allows the CPU to access information more quickly without waiting for main memory. Using CPU cache boosts performance and efficiency. Understanding caches demonstrates how computers may eliminate delays and perform programs faster. Buses in Von Neumann Architecture Buses are paths that connect the CPU, memory, and I/O devices. They’re like