Computer Hardware Components: A Beginner’s Easy Guide
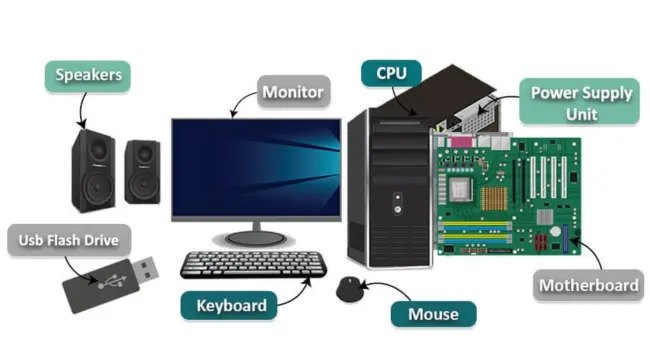
Every computer’s heart is its PC hardware. It has every part that can be grasped, such as the screen, keyboard, and CPU. This beginner’s guide to computer hardware will help you know every part. Learning about computer parts for beginners enhances your basic computer knowledge. It also increases computer literacy, allowing you to use technology with greater efficiency. You will know what causes a computer to run quickly or slowly. You will learn how different pieces interact. This tutorial will also assist you in choosing better hardware in the future. Knowing all of this makes using a computer more easy and enjoyable. What Are Computer Hardware Components? Computer hardware components are the physical parts that make up a computer, both inside and out. The CPU, RAM, storage devices, and motherboard are all crucial computer components. They are known as core components because they control computer performance. Without these, your computer cannot function. These components store your files, execute your applications, and display information on the screen. When you buy computer hardware, you are getting real, touchable items. Each component has a certain purpose, but when they work together, the computer becomes functional. Knowing them allows you to understand how computers work and how to keep them working well. Difference Between Hardware and Software The physical components of a computer are known as hardware. Its components are similar to computer CPUs. Software represents the mind. It uses a graphical user interface (GUI) to instruct the computer’s brain what to do. Definition and Characteristics of Hardware Hardware refers to the physical components of a computer. Examples include computer CPUs, memory sticks, motherboards, and hard drives. The central processing unit (CPU) is the computer’s brain. It performs the reasoning, problem-solving, and numerical computations. Every part has a purpose. The monitor displays photos. The keyboard produces letters. The mouse moves the pointer. These components work together to allow you to utilize the computer. You can store, replace, or enhance them as needed. Without hardware, the computer would not exist. Learning about hardware allows you to better comprehend the construction of a computer. Definition and Characteristics of Software Software is the part of the computer that cannot be touched. It contains programs, games, and applications. Software runs inside the computer, allowing it to perform important functions. You communicate with it using a graphical user interface (GUI). This means that you can give directions by clicking, typing, or tapping. The software instructs the hardware what to do. It allows you to write papers, watch videos, and play music. Without software, hardware cannot execute orders. Software can be upgraded or replaced to include new functionality. Knowing about software allows you to use your computer more effectively. How Hardware and Software Work Together Hardware and software function in tandem. Software delivers instructions to hardware, which then executes them. For example, when you click “print,” the software instructs the printer (hardware) to begin printing. Upgrades to computer hardware can sometimes improve the performance of software. Increasing memory can make games run faster. A better graphics card can enhance video quality. If the hardware is insufficient, software may run slowly. If the software is too advanced, old hardware may not perform properly. Understanding how they interact enables you to solve problems. It also assists you in selecting the appropriate upgrades for increased computer performance. Main Categories of Computer Hardware Components There are three major components to computer hardware. Internal components are found within the computer. Outside are accessories such as the keyboard and mouse. Networking components allow the computer connect to the internet. Each component has a specific purpose in ensuring the computer’s functionality. Internal Hardware Components Internal hardware components are those found inside your computer chassis. These include the CPU, which serves as the brain and regulates everything. Memory, or RAM, allows your computer to perform on multiple tasks at once. Storage devices such as hard disks and SSDs protect your contents. The motherboard connects all of these components and allows them to function together. Cooling systems such as fans keep the computer from overheating. To function properly, all of these internal components must be compatible, and they have an impact on how quickly and efficiently your computer performs. The CPU – The Heart of Your Computer The CPU is the main part that thinks and functions within a computer. It uses an approach known as the fetch-decode-execute cycle to follow orders step by step. The arithmetic logic unit (ALU) within the CPU performs logical and mathematical tasks. CPUs are classified into multiple groups, including x86 and ARM models. The clock speed, measured in gigahertz (GHz), indicates how quickly it operates. Some CPUs have many cores to do extra work. You can select a CPU based on what you want, ranging from low-end CPUs for basic tasks to high-end CPUs for gaming or complex applications. How the CPU Works The CPU behaves like a cook following a recipe. First, it retrieves the instructions. Then it decodes it so it knows what to do. Finally, it carries out the instruction. The ALU uses arithmetic and logic to solve issues. This cycle occurs rapidly, several times each second. The CPU’s cores allow it to accomplish multiple tasks at once. This process allows your computer to execute programs, play games, and do a variety of other tasks throughout the day. CPU Architecture and Clock Speed CPU architecture refers to the design of the CPU. There are two popular types: x86 and ARM. They function differently, but both help the computer run. Clock speed refers to how fast the CPU operates. It’s measured in gigahertz (GHz). The greater the GHz, the faster the CPU performs tasks. A faster clock speed results in greater performance for games and applications. The correct CPU architecture and clock speed are determined by what you want your machine to do. Choosing the Right CPU The proper CPU depends on your requirements. A low-end CPU is suitable for simple tasks such as browsing and writing. Mid-range CPUs can
Computer Hardware Components: A Beginner’s Easy Guide Read More »